Foreign Currency Trading 2024: What to Expect

Dear Clients and Partners,
On 8 February 2024, we examined how the exchange rates of the leading world currencies had changed in 2023 and discussed the key factors that will impact their performance in 2024. Additionally, we shared short and medium-term expert forecasts for the major currency pairs.
The strongest and weakest currencies in 2023
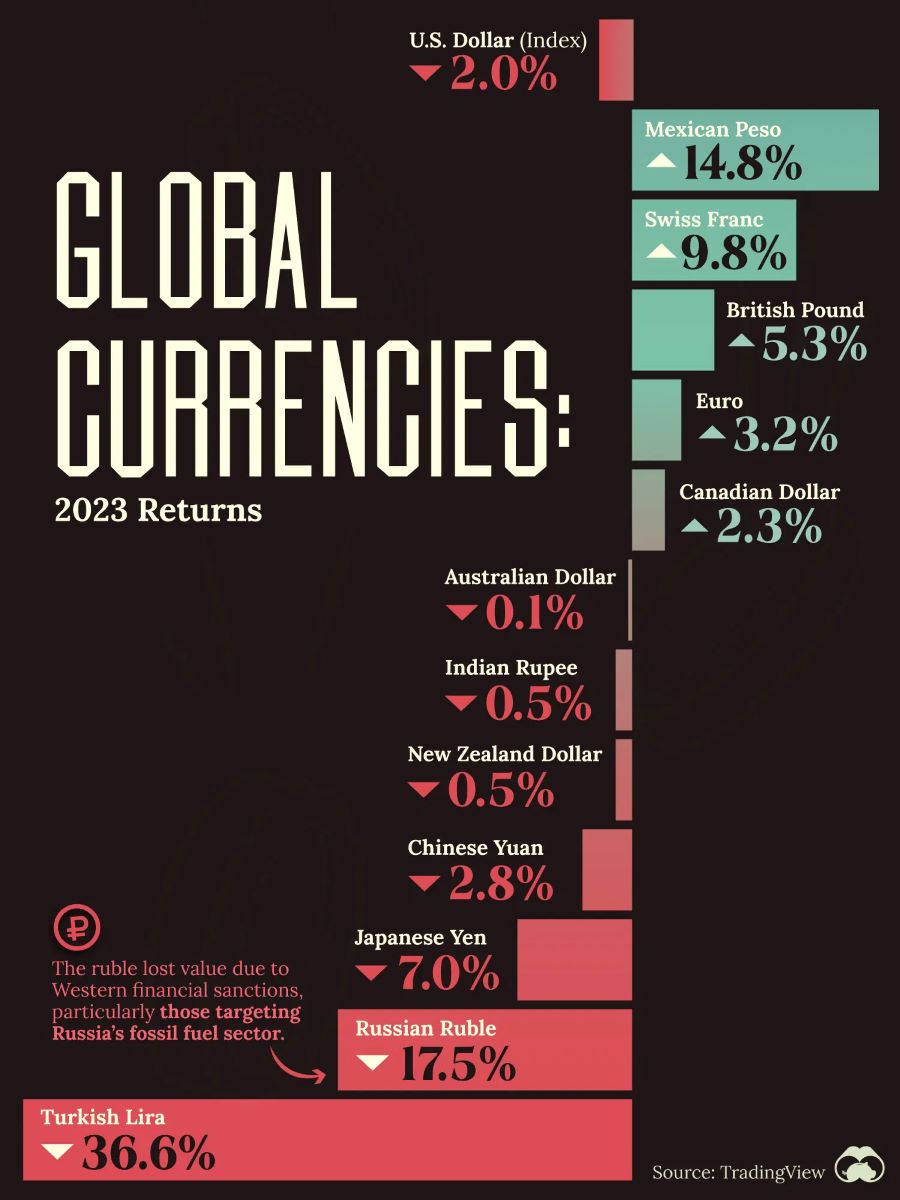
In 2023, many central banks were actively fighting inflation, resulting in relatively high volatility in the currency market. According to Visual Capitalist, the Mexican peso (MXN) saw an impressive increase last year, appreciating 14.8% against the US dollar (USD). This development occurred amid aggressive interest rate hikes by Mexico’s central bank. When writing, the interest rate was 11.25%.
The Swiss franc (CHF) also demonstrated steady growth of 9.8% due to geopolitical turbulence. The British pound (GBP), Canadian dollar (CAD), and euro (EUR) strengthened moderately within the range of 2-5% by year-end due to the interest rate hike policy pursued by the central banks.
The Australian dollar (AUD), New Zealand dollar (NZD), and Indian rupee (INR) ended the year with little to no changes, declining slightly by −0.1%, −0.5%, and −0.5%, respectively. The Chinese yuan (CNY) slid moderately by 2.8% in 2023.
The worst-performing currencies of the year were the Japanese yen (JPY), Russian ruble (RUB), and Turkish lira (TRY), which dropped by 7%, 17.5%, and 36.6%, respectively. The low-rate policy influenced the yen; the ruble is under pressure from the sanctions imposed following the onset of full-fledged war in Ukraine, and the lira is struggling due to domestic political and economic challenges.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), showing changes in the US currency value against a basket of the world’s major currencies, ended 2023 with a 2.0% decline.
Key factors influencing currencies in 2024
Inflation and central bank policy
The critical factor affecting exchange rates over the last two years was multiple central banks' aggressive interest rate hike cycles to combat inflation. The US regulator initiated these actions in Q1 2022, with the indicator increasing to 5.5% in less than two years.
Most of the world’s developed countries experienced monetary policy tightening to a similar extent. The Bank of England began to raise the interest rate at the end of 2021, a couple of months before the Federal Reserve, with the rate in the UK reaching 5.25% following 14 consecutive hikes. The European Central Bank began to increase the interest rate in mid-2022, pushing it up to 4.5%.
The central banks of Australia, Canada, and other countries followed suit, while the Bank of Japan was practically the only one among the most prominent regulators to pursue an adaptive zero-interest rate policy. This approach dominated the world for the first two years after the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
US elections
Historically, the US dollar exchange rate tends to rise under Democratic presidents and decline under Republicans. Therefore, the currency market becomes especially volatile in the face of uncertainty surrounding upcoming presidential elections in the US, as stated by Business Insider analysts. This event will determine not only the US policy but also the US dollar exchange rate against other currencies.
Donald Trump is expected to become the leading nominee from the Republican party, having won the primaries in the coming months. He will face incumbent Democratic President Joe Biden in a tightly contested election. Their rematch, accompanied by heated rhetoric and the potential for social conflict, may affect investor sentiment and currency markets. Trump is committed to higher tariffs, which will push up inflation and increase the US dollar exchange rate, putting the Chinese yuan, euro, and Mexican peso under pressure.
Trends in the global economy
The International Monetary Fund projects that global economic growth will remain at 3.1% in 2024 and rise to 3.2% in 2025. Higher rates and a withdrawal of fiscal support amid high debt exert pressure on economic activity.
In most regions, the inflation rate is slowing down faster than expected amid unwinding supply-related issues and restrictive monetary policy. Global inflation is projected to fall to 5.8% in 2024 and 4.4% in 2025, with the outlook for the next year being revised downwards.
Read more at R Blog - RoboForex
Sincerely,
The RoboForex Team




























